Clinical ctDNA research
RESEARCH IN THE CENTER
The ctDNA Center is committed to advancing and developing evidence-based research in ctDNA guided cancer treatment in Denmark by providing funding, establishing a national platform, and offering guidance.
Through the ctDNA Center, an ideal collaborative platform has been established, including clinicians and researchers. The aim is to elevate ctDNA research to the highest international standards. The overarching goal is to create an efficient framework for the optimal implementation of evidence-based ctDNA utilization in Danish Cancer Treatment.
Our research
Why perform clinical ctDNA research?
Clinical trials play a crucial role in guiding cancer treatment to each individual patient, and thereby reducing the risk of overtreatment and minimizing side effects. The primary objective of these trials is to provide the best possible treatment and cure for as many patients as possible. Throughout the trials, emphasis is placed on exploring implementation possibilities in the clinic and the very important factor, on enhancing patient quality of life.
The center is dedicated to advancing the field and strengthen the evidence-based research in ctDNA, including documentation for the optimal treatment choice for each patient. The aim is to extend the opportunity for participation in relevant clinical trials to alle eligible patients in Denmark.
The clinical trials focusing on the benefit of ctDNA guided cancer treatment are conducted at the local departments and institution across Denmark. This ensures that relevant patients are offered participation in a suitable trial during their ongoing treatment.
Important factors in the research
e
The aim of the research is to offer the best possible treatment and cure for as many patients as possible
Reduce overtreatment and side effects
Patient quality of life
Focused treatment
Structure
Organization of the research in the center
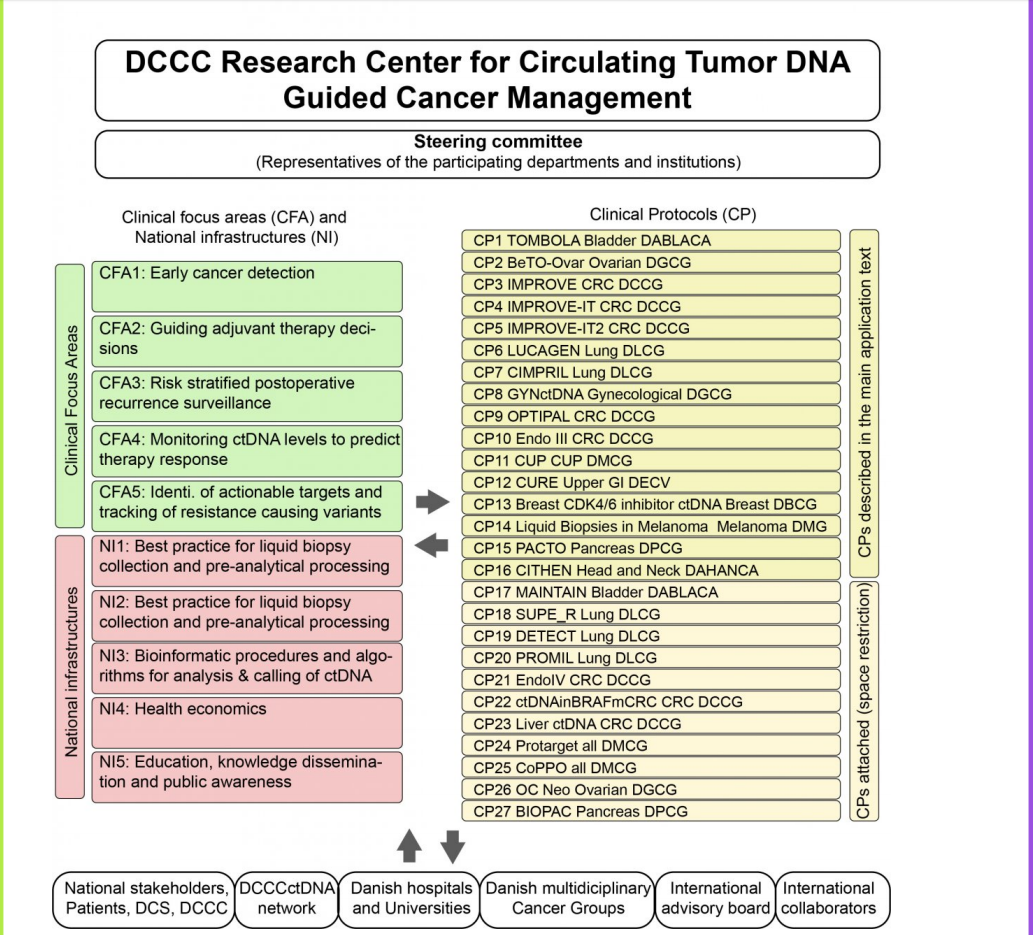
The research activities within the center are categorized into 5 Clinical Focus Areas (CFA) addressing cancer detection and treatment, and 5 National Infrastructures (NI), encompassing the entire process from sample collection to implementation in the clinic.
Additionally, there were 27 clinical protocols established initially when the center was established. Following, numerous protocols have been initiated.
National studies within the center
Projects in the National Infrastructures
In addition to the national clinical studies and protocols within the center, various other activities and projects are underway to enhance the foundation for ctDNA research.
Explore the carious projects listed below.
Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
National Infrastructure 1
NI1 makes guidelines to ensure uniform and high quality of plasma aiming for comparable results within and between trials. The Standard Operating Procedures (SOP) undergo continuous revision and are prepared by Regionernes Bio-og Genombank (RBGB).
Danish: SOP for blodprøvehåndtering ved ctDNA analyse RBGB
English: SOP for sampling, preparation and storage of plasma
SOP til håndtering af ascites prøver
See RBGB for more SOP: www.rbgb.dk
Pneumatic tube system transport
National Infrastructure 1
Pneumatic tube systems (PTSs) are widely used in most hospitals in Denmark, and their usage and scale are rapidly increasing, particularly due to the construction of larger hospitals. Despite their prevalence, few studies have been conducted to assess the impact of PTSs on the sensitivity of ctDNA analyses. The primary concern is the potential for contamination with high molecular weight DNA due to rupture of leukocytes.
Presently, an investigation of the PTSs is planned at Vejle Hospital (Department of Immunology and Biochemistry) and Aarhus University Hospital (Department of Clinical Biochemistry).
Different materials for cfDNA extraction
National Infrastructure 1
A questionnaire have been sent out to 86 members of the scientific group in RBGB to ask what material they use for cfDNA analysis.
The following materials are used besides plasma:
- Urine
- Bronchial wash
- Cerebrospinal fluid
- Ascites
Relevant laboratories have SOPs for sampling and preparation of the materials, which can be used by others when starting to work with these materials.
Long-term storage of material from clinical studies
National Infrastructure 1
Can retrospectively collected samples be used for future studies?
The effect of long-term storage of plasma, and the effect of storage temperature (-70oC vs -80oC) will be investigated. Examine samples in Danish Cancer Biobank/DCB (4 ml plasma) with matched high-quality samples taken during clinical trials (40 ml plasma). Yield?
Can plasma collected routinely through DCB be used for single mutation analyses e.g. KRAS? Exploring studies? Compare results obtained from DCB samples with results from IMPROVE samples. If yes, can they be used for NGS? Small panels/large panels? Old and newly collected samples as well as influence of handling time will be investigated.
Reference material for ctDNA detection
National Infrastructure 2
In the ctDNA center we have developed well-characterized reference material for ctDNA detection, consisting of cell line-derived background DNA and spike-in variants both enzymatically fragmented to ~167 bp-fragments. The reference material is flexible and the catalogue of available variants includes >100 relevant mutations (SNV, INDELS and fusions) from various human cancers including relevant drug targets. Further, the material spans over a wide noise profile and all possible SNV base substitution changes.
The reference material is designed to include variants frequently analyzed by ctDNA laboratories in Denmark and can be analyzed by using common methods like ddPCR and NGS. The final reference material is to be used as a quality assurance for ctDNA analyses among laboratories in Denmark as a way to obtain a common standard across laboratories and facilities.
The reference material is free and available for all members of the center.
The reference material is currently being used for the National Quality Assurance trial for ctDNA detection, but can also be used for:
- Bank of positive controls
- Quality certification program
- ctDNA methods benchmarking
- Methods development (pre-analytical, analytical, bioinformatics)
Contact Mads Heilskov Rasmussen (mads.heilskov@clin.au.dk) or Maria Hønholt Jørgensen (mhj@clin.au.dk) if you are interested in the reference material.
Database on ddPCR ctDNA assays
National Infrastructure 2
Niels Pallisgaard and Malene Green Madsen from Næstved are building a database with the ddPCR assay information described below. The information is a collection of assays from ctDNA laboratories across the country. The assays will be available for the ctDNA Center laboratories for free, except for the transportation costs.
An assay database will save time, money, and work when an assay in the database is needed in ddPCR in the detection and monitoring of clinical samples. As the database grows the ctDNA laboratories will need to develop and validate fewer and fewer assays over time, thus saving resources.
Information included in the database:
- Contact lab(s) who have used the assay
- PCR conditions
- Primer and probe sequences and concentrations (if known)
- Available controls
- Picture of 2D plot
- LoB and LoD if available
- Traffic light scoring (red: only used a few times in a single lab, yellow: used in several labs, green: widely used
Database will be made available for the ctDNA research center members.
Quality assurance program on ctDNA purification
National Infrastructure 2
Niels Pallisgaard and Malene Green Madsen lead a quality assurance program on ctDNA purification. Plasma samples will be prepared centrally and distributed to ctDNA laboratories who purify the ctDNA samples and send them back to Næstved laboratory. Næstved laboratory analyses ctDNA samples for different parameters like yield, degree of single strandedness, protinaseK carryover, fragmentation - and the participating labs will receive a report with individualized comments.
If you are working in a lab and want to participate in the EQA, write an e-mail to Malene Green Madsen.
Pipeline for targeted sequencing of cfDNA data with UMIs
National Infrastructure 3
The UMIs can help remove PCR errors from deep sequenced data.
Measuring quality of life in cancer
National Infrastructure 4
Mapping EORTC QLQ-C30 on to EQ-5D-5L
- 2000+ cancer patients (all cancers) surveyed x4 over one year with QLQ-C30 and EQ-5D-5L
- Data linked to registers for demographics, healthcare utilization, health status, etc.
- Goal: map EORTC on to EQ-5D to get an algorithm for calculating QALYs without weights
Compare instruments for QoL in Danish Cancer patients
- Danish value set for EORTC QLQ-C10D (subset of QLQ-C30 for calculating QALYs) about to be published
- Goal: compare QALY estimates produced by EQ-5D-5L, QLQ-C10D value set and the mapping algorithm to establish the most suitable way of measuring QoL in Danish cancer patients
Inequalities in cancer
National Infrastructure 4
Socioeconomic status and quality of life
- Comparing quality of life and access to services in cancer patients across the socio-economic gradient
- Education, income, region.
Distributional cost-effectiveness evaluations (DCEA):
- Looking at how ctDNA interventions impact on not only the efficiency, but also equity
- Innovative statistical method to combine the two concepts of efficiency and equity
Working group
Standardization Team
The national working group is currently developing a paper focused on standardizing purification, detection, and reporting results in ctDNA analyses. This paper will encompass recommendations for the handling of blood samples prior to extraction, quality control (QC) of extracted DNA before ctDNA analysis, assay validation, process control, internal controls and external quality assessment.
Reach out if you have any questions regarding this.
National network
ctDNA RECIST
In the context of metastatic cancers, decisions regarding systemic palliative therapies often rely on the Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST), a method primarily utilizing imaging. With Karen-Lise Garm Spindler in front, a network proposes a ctDNA-RECIST instead, a response classification based on circulating tumor DNA measurements and its confidence intervals. They aim to raise the topic for discussion.


Curious to learn more?
Publications
Circulating tumor DNA: Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors - can we RECIST? Focus on colorectal cancer
Karen-Lise Garm Spindler, Anders Jacobsen
(2023, April). Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology, vol 15. Pages 1-11. Doi: 10.1177/17588359231171580
ctDNA-Response evaluation criteria in solid tumors - a new measure in medical oncology
Anders K. M. Jakobsen, Karen-Lise Garm Spindler
(2023, February). European Journal of Cancer, 180. Pages 180-183. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2022.11.039. PMID: 36610263
We are grateful for your participation in our clinical research
Patients
Patient participation in clinical research studies is of utmost importance to advance the field further. Our dedication is focused on advancing cancer treatment through ctDNA guided intervention and improving treatment for cancer patients. We sincerely appreciate the participation of our patients.
We recognize and understand the challenges and situations patients face when diagnosed with cancer, thus we prioritize the patients’ comfort, privacy, and health throughout the clinical research projects. Your insights and participation contribute to groundbreaking research findings, that have the potential to shape the future of cancer treatment.
Thank you!
As there is currently no evidence that guiding treatment using ctDNA (and CTC) leads to improved tre atment efficacy and outcomes, these measurements are not yet part of the standard of care in Denmark. In the ctDNA Center, we are actively engaged in clinical trials aiming to determine the potential benefits of measuring ctDNA, and they show promising results. Until these trials are completed, which unfortunately may take 3-5 years, ctDNA measurements are only offered in the context of these trials.
You are offered participation in a clinical trial at the hospitals, when you start treatment, if there is a clinical trial suitable for your situation.
Find more research
Read more about the ctDNA research
Clinical Focus Areas + National Infrastructures
Read more about the focus and the leaders
Funded projects
Get inspired from other clinical studies
Publications
Find the publications published in the center
Research collaboration in the center
Learn what the center can help you with
ADDRESS FOR THE SECRETARIAT
Science Center Skejby, MOMA
Brendstrupgårdsvej 21, build. A
8200 Aarhus N
CONTACT
ctDNA@clin.au.dk
+45 78 45 53 39